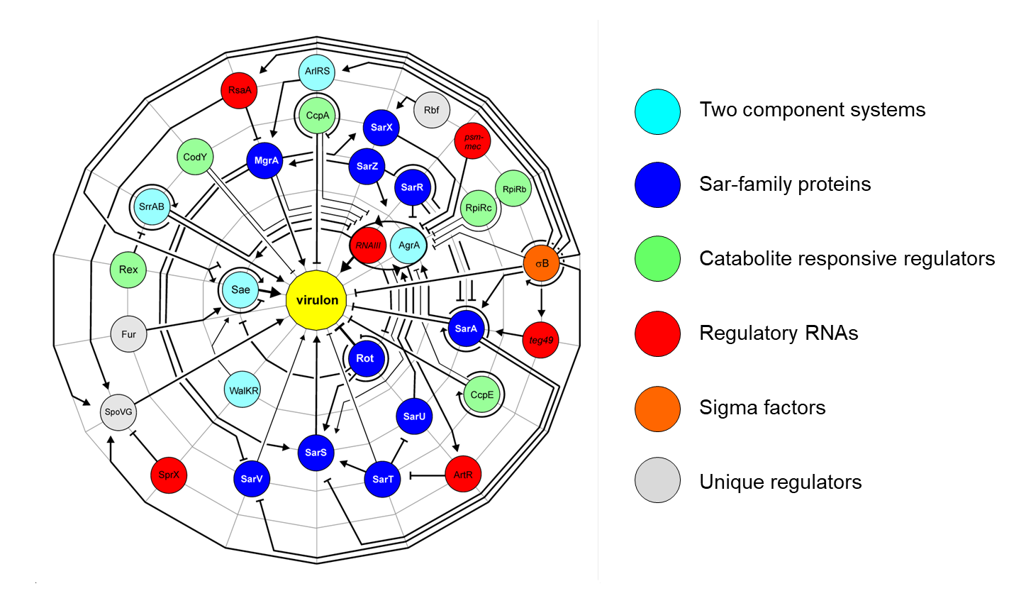
Regulatory systems affecting infectivity and immune evasion of bacteria in mammal hosts
A prominent member of the group of nosocomial bacteria is Staphylococcus aureus, a common colonizer of our nasopharyngeal area and the skin, and at the same time a feared opportunistic pathogen in the healthcare setting. Especially in immunocompromised people, S. aureus is able to cause live-threatening diseases such as endocarditis, osteomyelitis, and sepsis. The Gram-positive bacterium is equipped with a large armamentarium of virulence factors and a sophisticated network of regulatory molecules allowing it to rapidly respond to environmental changes encountered within the host during the infection process. In this part of our research activities at IMMH, we are interested in identifying and characterizing regulatory factors and phosphorylation systems involved in pathogenesis of S. aureus. We are specifically interested in regulators that link virulence factor synthesis with the metabolic activity of the bacterial cell. Another major focus of our staphylococcal research are protein kinase/phosphatase systems and their impact on infectivity. Potential genes of interest will be inactivated by genetic engineering, and resulting mutants characterized in a variety of in vitro (i.e. biofilm assays, growth kinetic studies, metabolomics, transcriptomics, and cell culture-based adhesion and invasion/persistence studies) and in vivo assays (i.e. murine infection models). Another major pillar of this part of IMMH research are bacterial secretion factors, with a special focus on how the host recognizes them, and which immune response(s) are triggered.
Scientists and students interested in this topic are warmly welcome to collaborate with us in this exciting research field. If you are interested, please get into contact with us.
Extracellular Release of a Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase Correlates With Periodontal Disease Severity
Ahmad Aljohmani, Hakon Heinze, Federico Guillermo Gharzia, Bashar Reda , Ahmed Mohamed Mostafa Abdrabou, Sören L Becker, Markus Bischoff, Matthias Hannig, Daniela Yildiz (2024)
J Clin Periodontol. 52(2):237-248
DOI: 10.1111/jcpe.14073
The secreted tyrosine phosphatase PtpA promotes S. aureus survival in RAW 264.7 macrophages through decrease of the SUMOylation host response
Nadhuma Youssouf, Marianne Martin, Markus Bischoff, Philippe Soubeyran, Laila Gannoun-Zaki, Virginie Molle (2023)
Microbiol Spectr. 11:e0281323
The transcription factor SpoVG is of major importance for biofilm formation of Staphylococcus epidermidis under in vitro conditions, but dispensable for in vivo biofilm formation
Hannah Benthien, Beate Fresenborg, Linda Pätzold, Mohamed Ibrahem Elhawy, Sylvaine Huc-Brandt, Christoph Beisswenger, Gabriela Krasteva-Christ, Sören L. Becker, Virginie Molle, Johannes K. Knobloch, Markus Bischoff (2022)
Int J Mol Sci. 23:3255
DOI: 10.3390/ijms23063255
Bitter taste signaling in tracheal epithelial brush cells elicits innate immune responses to bacterial infection
Monika I. Hollenhorst, Rajender Nandigama, Saskia B. Evers, Igor Gamayun, Noran Abdel Wadood, Alaa Salah, Mario Pieper, Amanda Wyatt, Alexey Stukalov, Anna Gebhardt, Wiebke Nadolni, Wera Burow, Christian Herr, Christoph Beisswenger, Soumya Kusumakshi, Fabien Ectors, Tatjana I. Kichko, Lisa Hübner, Peter Reeh, Antje Munder, Sandra-Maria Wienhold, Martin Witzenrath, Robert Bals, Veit Flockerzi, Thomas Gudermann, Markus Bischoff, Peter Lipp, Susanna Zierler, Vladimir Chubanov, Andreas Pichlmair, Peter König, Ulrich Boehm, Gabriela Krasteva-Christ (2022)
J Clin Invest. 132(13):e150951
DOI: 10.1172/JCI150951
Protein disulfide isomerase and extracellular adherence protein (Eap) cooperatively potentiate staphylococcal invasion into endothelial cells
Marleen Leidecker, Anne Bertling, Muzaffar Hussain, Markus Bischoff, Johannes A. Eble, Anke C. Fender, Kerstin Jurk, Christine Rumpf, Mathias Herrmann, Beate E Kehrel, Silke Niemann (2023)
Microbiol Spectr.11:e0388622
Staphylococcus aureus extracellular adherence protein (Eap) reduces immune cell phenotype in developing but not in established atherosclerotic lesions
Manuel Salzmann, Harald Platzer, Marion Mussbacher, Martina Derler, Max Lenz, Patrick Haider, Mira Brekalo, Julia B. Kral-Pointner, Stefan Kastl, Walter S. Speidl, Klaus T. Preissner, Uwe Schubert, Markus Bischoff, Pavel Uhrin, Johann Wojta, Philipp J. Hohensinner (2023)
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1869(3):166616
Characterization of the secreted acid phosphatase SapS reveals a novel virulence factor of Staphylococcus aureus that contributes to survival and virulence in mice
Nour Ahmad-Mansour, Mohamed Ibrahem Elhawy, Sylvaine Huc-Brandt, Nadhuma Youssouf, Linda Pätzold, Marianne Martin, Noran Abdel-Wadood, Ahmad Aljohmani, Madjid Morsli, Gabriela Krasteva-Christ, Sören L. Becker, Daniela Yildiz, Jean-Philippe Lavigne, Laila Gannoun-Zaki, Markus Bischoff, Virginie Molle (2022)
Int J Mol Sci. 14;23:14031